SQL Health Dashboard
Exploring
The SQL Health Dashboard provides SYSPRO Administrators and SQL Database Administrators a one-stop-shop for viewing and managing the system for high availability.
The dashboard displays information on both the system and company databases to assist in identifying potential problems, as well as enabling the repair of certain issues found within the databases.
The SQL Health dashboard provides the following functionality:
- Single view of all your SYSPRO databases
- Repair capability on certain issues found (e.g. creation of missing tables/columns)
- Insights providing at-a-glance values and drill-down capabilities
Information displayed includes:
- Configuration information for the SQL instance and each SYSPRO database
- Information on the database and log files, including the size, free space and growth options
- User access and permissions
- Non-SYSPRO objects that interact with and which are dependent on SYSPRO data (i.e. stored procedures, views, triggers. etc.)
- Fragmentation of SYSPRO indexes
- SYSPRO table, column, index and foreign key information
-
This program is accessed from the Program List pane of the SYSPRO menu.
Program List > Utilities > SQL Server Utilities > SQL Health Dashboard
This refers to a set of rules determining how data is compared and sorted.
Besides determining the alphabet, the collation order also determines whether accents, case and other alphabet properties are considered in the sort order. For example: if the collation is case-sensitive, the uppercase letters are sorted before the lowercase letters.
Binary sort order is case-sensitive (i.e. lowercase precedes uppercase) and accent-sensitive. This is the fastest sorting order.
A compatibility level sets certain database behaviors to be compatible with the specified version of SQL Server.
If your compatibility level is set to an older version of SQL then this can result in performance issues.
SQL Server fragmentation occurs when data is sorted in a non-contiguous way.
Index fragmentation is an expected and unavoidable characteristic of any OLTP environment.
Fragmentation is defined as any condition which causes more than the optimal amount of disk I/O to be performed in accessing a table, or causes the disk I/O's that are performed to take longer than optimal.
SQL Server backup and restore operations occur within the context of the recovery model of the database.
Recovery models are designed to control transaction log maintenance.
A recovery model is a database property that controls how transactions are logged, whether the transaction log requires (and allows) backing up, and what kinds of restore operations are available.
Three recovery models exist:
- Simple
- Full
- Bulk-logged
Typically, a database uses the full recovery model or simple recovery model.
A database can be switched to another recovery model at any time.
Starting
- SYSPRO 8 2018 R2 onwards
- The following database information is not available through the SQL Health Dashboard:
- Point of Sale (PoS)
- Manufacturing Operations Management (MOM)
- The following is not verified on any databases that are not on the same version as the system database (which is assumed to be current):
- Tables
- Columns
- Indexes
- Foreign keys
- Certain issues found and displayed in the dashboard (e.g. index fragmentation) cannot be corrected in the dashboard, as these must be addressed as part of your SQL maintenance plan
Solving
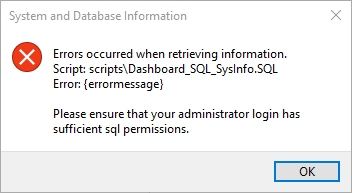
This typically indicates that the administrator login doesn't have sufficient SQL permissions to run certain functions.
The program will close.
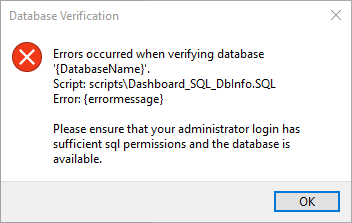
This typically indicates that the administrator login doesn't have sufficient permission to run certain functions.
The program will skip any further processing of that particular database and continue to the next database in the list (if there is one).
The SQL Instance Information pane is automatically hidden and can be accessed from the right-hand side of the screen.
We advise that you use the latest version of SQL in order to leverage the latest improvements.
We advise that you use the highest compatibility level available for your version of SQL, in order to leverage the latest improvements.
Unless memory is capped, SQL will use all available memory on a server. This can result in performance issues, especially when SQL exists on the same server as the applications that use it.
If the database version against a company is not the same as the database version on the system database, then no validation is performed on tables, columns, indexes or foreign keys as these will need to be upgraded.
This can be remedied by logging into the company linked to the database which will then process any minor database upgrades required.
Fragmentation of indexes in SQL can lead to performance degradation. We therefore recommend that you add a task to REBUILD or REORGANISE the indexes in the database to your SQL Maintenance Plan.
Your account login should either be a member of the sysadmin fixed server role, or a member of the db_owner role on each of the SYSPRO databases.
Using
-
Unless memory is capped, SQL will use all available memory on a server.
This can result in performance issues, especially when SQL exists on the same server as the applications that use it.
- The collation used against any SYSPRO database must be case-sensitive.
Referencing
The SYSPRO Databases pane lists all databases identified in the system database itself (including the system database).
An icon in the Company column quickly identifies if a database is found to contain any issues.
The Database Details pane displays relevant information regarding the SYSPRO database selected in the SYSPRO Database pane, as well as physical files for the selected SYSPRO database.
|
Column |
Detail |
|---|---|
|
Repair Issues |
Select this to begin the repair function for issues found against:
|
|
Company |
Indicates the company ID. |
|
Name |
Indicates the company name. |
|
Database |
Indicates the SYSPRO database name. |
|
Version |
Indicates the SYSPRO database version. If the database version against a company is not the same as the database version on the system database, then no validation is performed on tables, columns, indexes or foreign keys as these will need to be upgraded. This can be done by logging into the company linked to the database. |
|
Collation |
The collation used against any SYSPRO database must be case-sensitive. |
|
Compatibility level |
The compatibility level plays an important role in determining what mechanisms SQL uses in processing and, if set lower than the compatibility level for the version of SQL you are running, this can lead to performance issues. |
|
Recovery model |
Indicates the recovery model, used to control transactional log maintenance. |
|
Auto close |
Indicates if the option is enabled on the database. This must not be set on SYSPRO databases.
|
|
Auto shrink |
Indicates if the option is enabled on the database. Having this switched on can cause performance issues. |
|
Auto create statistics |
Indicates whether the option is enabled on the database. |
|
Auto update statistics |
Indicates whether the option is enabled on the database. The
auto create and update statistics do affect performance insofar as statistics
are used in the SQL query optimizer.
|
|
Status |
This reflects the status of the database at the time that the query was loaded (e.g. ONLINE). If this status reflects as anything other than ONLINE, then the checks on tables, columns, indexes, etc. are not carried out. Possible database states include:
|
|
Read only |
Indicates if the option is enabled on the database. SYSPRO databases should never be
set to read only.
|
|
Last full backup |
Indicates the date and time of last full backup. |
|
Last log backup |
Indicates the date and time of last log backup. |
The following information regarding the physical files for the selected SYSPRO database is included in the Database Details pane:
- Logical name
- Type (i.e. Data/Log)
- Physical Location
- Size (MB)
-
Growth setting (e.g. 10 % or 1 MB)
It is important that the growth setting on these files is set correctly as this does have a performance impact.
- Maximum size allowed
- Space Used (MB)
- Free space in file (MB)
-
Free space %
Monitoring of free space within tables is important as it has a bearing both on the growth and the maximum size of the table.
The bottom pane of the dashboard displays information found during the inspection and repair process, and relates to the following:
- Tables
- Columns
- Indexes
- Foreign Keys
- Object Dependencies
- Index Fragmentation
- SQL Users
The following checks are performed against the company databases' tables. Results are displayed in the Tables pane:
| Check/Message | Definition | Repairable? |
|---|---|---|
|
Standard table missing |
A table defined in the data dictionary does not exist in the database. |
Yes |
|
Standard custom form table missing |
A definition for custom form information exists, however the table is not in the database. |
Yes |
|
User defined table |
A table exists in the database that is not defined in the data dictionary. |
No Informational only |
|
User defined custom form table |
A table ending in “+“ exists and this is not a standard custom form table. |
No Informational only |
The following checks are performed against the company databases' columns. Results are displayed in the Columns pane:
| Check/Message | Definition | Repairable? |
|---|---|---|
|
Standard column missing |
A column defined in the data dictionary is missing from the SYSPRO table. |
Yes |
|
Standard custom form column missing |
A custom form column is missing from the table. |
Yes |
|
User defined column |
A user defined column exists in a standard SYSPRO table. |
No Informational only |
|
User defined custom form column |
A user defined column exists in the custom form table. |
No Informational only |
|
Column definition does not match SYSPRO definition |
A column's definition (type, size, collation, default, nullable) does not match what is expected. |
Yes |
|
Custom form column definition does not match SYSPRO definition |
A custom form column's definition (type, size, collation, default, nullable) does not match what is expected. |
Yes |
|
User defined column not nullable and has no default constraint |
A user defined column in a standard table does not have a default and is not nullable. This will cause issues when trying to insert a row into the table. |
Yes |
|
User defined custom form column not nullable and has no default constraint |
A user defined column in a custom form table does not have a default and is not nullable. This will cause issues when trying to insert a row into the table. |
Yes |
The following checks are performed against the company databases' indexes. Results are displayed in the Indexes pane:
| Check/Message | Definition | Repairable? |
|---|---|---|
|
Standard index missing |
A missing index can lead to performance issues. In addition, if the missing index is the primary key, then this can lead to loss of data integrity. |
Yes |
|
Standard custom form index missing |
A missing index can lead to performance issues. In addition, if the missing index is the primary key, then this can lead to loss of data integrity. |
Yes |
|
User defined index |
User defined index exists on SYSPRO table. |
No Informational only |
|
User defined custom form index |
User defined index exists on custom form table. |
No Informational only |
|
Index column mismatch |
The index does not contain the columns SYSPRO expects and can lead to performance issues. |
Yes |
|
Custom form index column mismatch |
The index does not contain the columns SYSPRO expects and can lead to performance issues. |
Yes |
|
Index defined against incorrect table |
This occurs when an existing table is renamed without deleting the indexes, etc. and will prevent the creation of the index against the correct table. |
Yes |
|
Custom form index defined against incorrect table |
This occurs when an existing table is renamed without deleting the indexes, etc. and will prevent the creation of the index against the correct table. |
Yes |
|
User defined primary key |
A standard table has a primary key defined that is not what is expected by SYSPRO. This can and will lead to data integrity issues. |
Yes |
|
User defined custom form primary key |
A standard table has a primary key defined that is not what is expected by SYSPRO. This can and will lead to data integrity issues. |
Yes |
The following checks on foreign keys are performed against the company databases. Results are displayed in the Foreign Keys pane:
| Check/Message | Definition | Repairable? |
|---|---|---|
|
Standard foreign key missing |
A foreign key linking standard SYSPRO tables is missing. |
Yes |
|
User defined foreign key |
A user defined foreign key has been defined against a SYSPRO table and has been created with the NOCHECK directive. |
No Informational only |
|
Standard foreign key is enabled |
A standard foreign key has been enabled. SYSPRO uses foreign keys created with the NOCHECK directive, which means that the foreign key is not used for data integrity purposes as SYSPRO performs its own data integrity verification. |
Yes |
|
User defined foreign key is enabled |
A user defined foreign key has been defined against a SYSPRO table. We strongly discourage you from adding your own Foreign Keys to a SYSPRO database (especially without the NOCHECK directive) as this could cause SYSPRO applications to fail unexpectedly. |
No SYSPRO doesn't know the purpose of the user defined foreign key, so won't change
it in any way. It's your responsibility to address as you see fit.
|
|
Foreign key defined against incorrect table |
A named foreign key exists against the incorrect table. This will prevent the creation of the same key against the correct tables. |
Yes |
|
Foreign key column mismatch |
A foreign key's definition does not match what is expected by SYSPRO. |
Yes |
After the program completes its checks on the databases, the following list is returned containing all user defined objects (i.e. views, stored procedures, etc.) that are dependent on both standard SYSPRO and custom form tables and columns:
| Column | Detail |
|---|---|
|
Table |
Indicates the SYSPRO table. |
|
Column |
Indicates the SYSPRO column. |
|
Schema |
Indicates the schema in which the object is defined. |
|
Name |
Indicates the name of the object. |
|
Object Type |
Indicates the type of object (e.g. View, Stored procedure, Trigger). |
|
Selected |
Indicates whether the column is selected (e.g. SELECT StockCode). |
|
Selected all |
Indicates whether the column is selected using a wildcard (e.g. SELECT *). |
|
Updated |
Indicates that the column is updated by the object and is flagged as a warning. We strongly
advise against updating SYSPRO data outside of the software, as any change
may not follow the business rules associated with the data.
|
Index fragmentation and out of date statistics can have a significant effect on performance. Therefore, this pane displays the following:
- Indexes in SYSPRO that are fragmented by more than 5 percent
- Indexes' statistics that have not been updated in the last 30 days
No repair function is available as it is recommended that the rebuilding or reorganization of an index, as well as the updating of statistics, is performed when the database is not in use.
| Column | Detail | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Table |
Indicates the SYSPRO table. |
||||||||
|
Index |
Indicates the SYSPRO index. |
||||||||
|
Fragmentation % |
Indicates the percentage of fragmentation. |
||||||||
|
Page Count |
Indicates the number of pages occupied by the index. If this is a low
count then it is possible that SQL will not rebuild or reorganize the index.
|
||||||||
|
Rows in Table |
Indicates the number of rows in the table. If this is a low
count then it is possible that SQL will not rebuild or reorganize the index.
|
||||||||
|
Statistics updated |
Indicates the date and time that the statistics for this index were last updated. SQL will automatically update these depending on usage. If the date and time is set as 1900-01-01 0:00:00.00 then the statistics have never been updated. |
||||||||
|
Suggested function |
Indicates the function that Microsoft suggests to run.
|
After the program completes its checks on the databases, the following list is returned detailing all users that have access to the database, as well as their permission levels:
|
Column |
Detail |
|---|---|
|
User |
Indicates the user defined against the database. Any sysadmin logins will be returned as
blank due to them having full access to the database and not requiring a link
to a specific user.
|
|
Login |
Indicates the login that the user is linked to. |
|
Type |
Indicates the type of login (e.g. WINDOWS_LOGIN or SQL_LOGIN) |
|
Permissions |
Indicates the user's permissions as a comma separated list (e.g. db_datareader, db_datawriter, sysadmin) |
This pane is automatically hidden and can be accessed from the right-hand side of the screen.
The dashboard displays the following pertinent information regarding the SQL instance that SYSPRO 8 is using:
- SQL instance name
- SQL version
- Default collation for the SQL instance
- Minimum memory allocated to SQL
- Maximum memory allocated to SQL
- Amount of physical memory on the server
- Date and time SQL started